Since its introduction, Aadhaar has become the cornerstone of identity verification across various sectors. But traditionally, verifying Aadhaar details required an OTP sent to the individual’s registered mobile number. However, this method has its limitations, especially when users lack access to their registered mobile numbers or face connectivity issues. To address these challenges, Aadhaar Verification API came as the solution, enabling verification without the need for an OTP. This advancement not only streamlines the verification process but also enhances user convenience and broadens accessibility.
The adoption of Aadhaar Verification APIs has seen significant growth. In March 2023 alone, Aadhaar authentication transactions climbed to 2.31 billion, indicating a robust increase in digital verifications. Furthermore, Aadhaar-based face authentication transactions reached an all-time high of 10.6 million in May 2023, showcasing the increasing preference for biometric verification methods. These statistics underscore the pivotal role of Aadhaar Verification API in facilitating secure and efficient identity verification without relying on OTPs.
Challenges with OTP based verification
While One-Time Passwords (OTPs) have been widely adopted for authentication, they present several challenges that can compromise security and user experience:
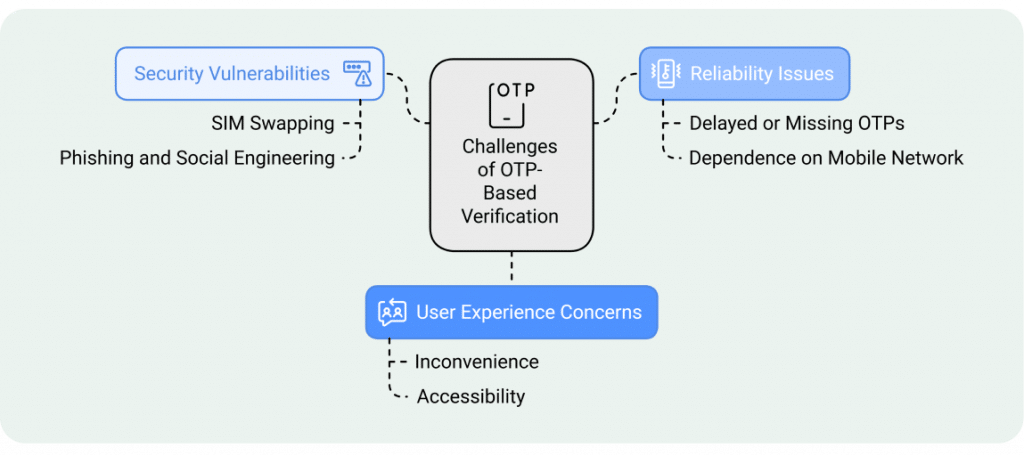
- Security Vulnerabilities:
- SIM Swapping: Attackers can perform SIM swap attacks to intercept OTPs sent via SMS, gaining unauthorized access to user accounts.
- Phishing and Social Engineering: Cybercriminals employ phishing techniques to trick users into revealing OTPs, leading to potential breaches.
- Reliability Issues:
- Delayed or Missing OTPs: Network issues can cause significant delays in OTP delivery, frustrating users and hindering timely access.
- Dependence on Mobile Network: Users in areas with poor network coverage may face challenges receiving OTPs, affecting accessibility.
- User Experience Concerns:
- Inconvenience: The need to retrieve and input OTPs for each authentication can be cumbersome, leading to user dissatisfaction.
- Accessibility: Individuals without access to their registered mobile numbers or those traveling internationally may struggle with OTP-based verification.
These challenges highlight the need for more secure and user-friendly authentication methods, prompting organizations to explore alternatives to traditional OTP-based systems.
Mechanisms of OTP-less Aadhaar Verification
Verifying Aadhaar without the traditional One-Time Password (OTP) has become increasingly accessible, thanks to alternative methods that ensure both security and user convenience. These mechanisms are particularly beneficial in scenarios where users may not have access to their registered mobile numbers or face connectivity challenges.
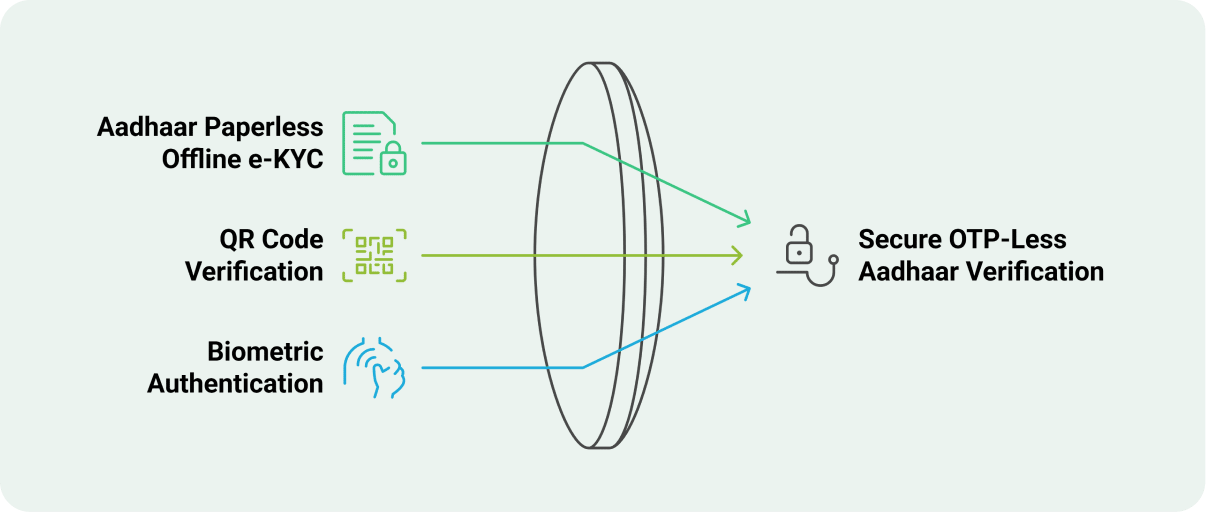
Aadhaar Paperless Offline e-KYC
This method allows individuals to download an XML file containing their Aadhaar details from the UIDAI website. The file is secured with a password set by the user and can be shared with service providers for identity verification. Since this process is offline, it eliminates the need for OTPs and internet connectivity.
QR Code Verification
Aadhaar cards feature a QR code that encapsulates the holder’s demographic information. Service providers can scan this QR code using authorized applications to retrieve and verify the individual’s details instantly. This method bypasses the need for OTPs and is particularly useful in in-person verification scenarios.
Biometric Authentication
Leveraging biometric data such as fingerprints or iris scans, this method verifies an individual’s identity by matching the provided biometric information with the data stored in the Aadhaar database. This approach is highly secure and eliminates the dependency on mobile networks and OTPs.
By adopting these OTP-less verification mechanisms, organizations can enhance the efficiency of their onboarding processes while maintaining robust security standards.
Considerations with Aadhaar Verification API
Implementing Aadhaar Verification APIs offers numerous advantages; however, organizations must navigate several challenges to ensure security, privacy, and compliance:
- Data Security and Privacy
- Data Breaches: Despite robust measures, Aadhaar’s centralized database has experienced security breaches. In early 2018, unauthorized access to demographic data was reportedly obtained for a nominal fee, exposing sensitive information of Indian citizens.
- Third-Party Vulnerabilities: When businesses integrate Aadhaar KYC through third-party providers, the security of user data can become dependent on these intermediaries, potentially increasing the risk of unauthorized access.
- Regulatory Compliance
- Adherence to UIDAI Guidelines: Organizations must comply with the Unique Identification Authority of India’s (UIDAI) regulations, including implementing Aadhaar Data Vaults to securely store Aadhaar numbers in encrypted formats, ensuring restricted access and preventing unauthorized usage.
- System Reliability and Accessibility
- Authentication Failures: Biometric authentication methods, such as fingerprint and iris scans, can face challenges due to issues like poor fingerprint quality or device malfunctions, leading to authentication failures.
- Infrastructure Limitations: In regions with limited internet connectivity or technological infrastructure, accessing Aadhaar Verification services can be challenging, affecting the inclusivity of such digital solutions.
- User Consent and Data Usage
- Informed Consent: Ensuring that individuals are fully informed about how their Aadhaar data will be used and obtaining explicit consent is crucial to maintain trust and comply with privacy standards.
- Data Minimization: Collecting only the necessary data points required for verification purposes is essential to reduce the risk of misuse and enhance data protection.
Addressing these challenges necessitates a multifaceted approach, including implementing advanced security protocols, conducting regular audits, providing user education, and staying abreast of evolving regulatory requirements. By proactively managing these considerations, organizations can leverage Aadhaar Verification API effectively while safeguarding user data and maintaining compliance.
Conclusion
The Aadhaar Verification API’s impact extends beyond mere numbers. By automating verification processes, businesses have reported up to 50% cost savings, reducing reliance on manual methods. Moreover, the cumulative Aadhaar authentication transactions in India reached over 94 billion in the fiscal year 2023, highlighting the system’s robustness.
However, as with any technological advancement, it’s essential to approach with a blend of enthusiasm and caution. While the Aadhaar Verification API offers efficiency and scalability, organizations must remain vigilant about data privacy and security.
After all, with great power comes great responsibility!